IEFC General Assembly 2025 in San Sebastián

The IEFC Annual General Meeting 2025, co-organised by IEFC, USSE, HAZI, NEIKER, Cesefor and Gipuzkoa, took place on 8th and 9th April in the city of San Sebastián (Donostia) in

European Institute of Planted Forest – IEFC
The multi-actor network for sustainable management and resilience of planted forests

The IEFC Annual General Meeting 2025, co-organised by IEFC, USSE, HAZI, NEIKER, Cesefor and Gipuzkoa, took place on 8th and 9th April in the city of San Sebastián (Donostia) in
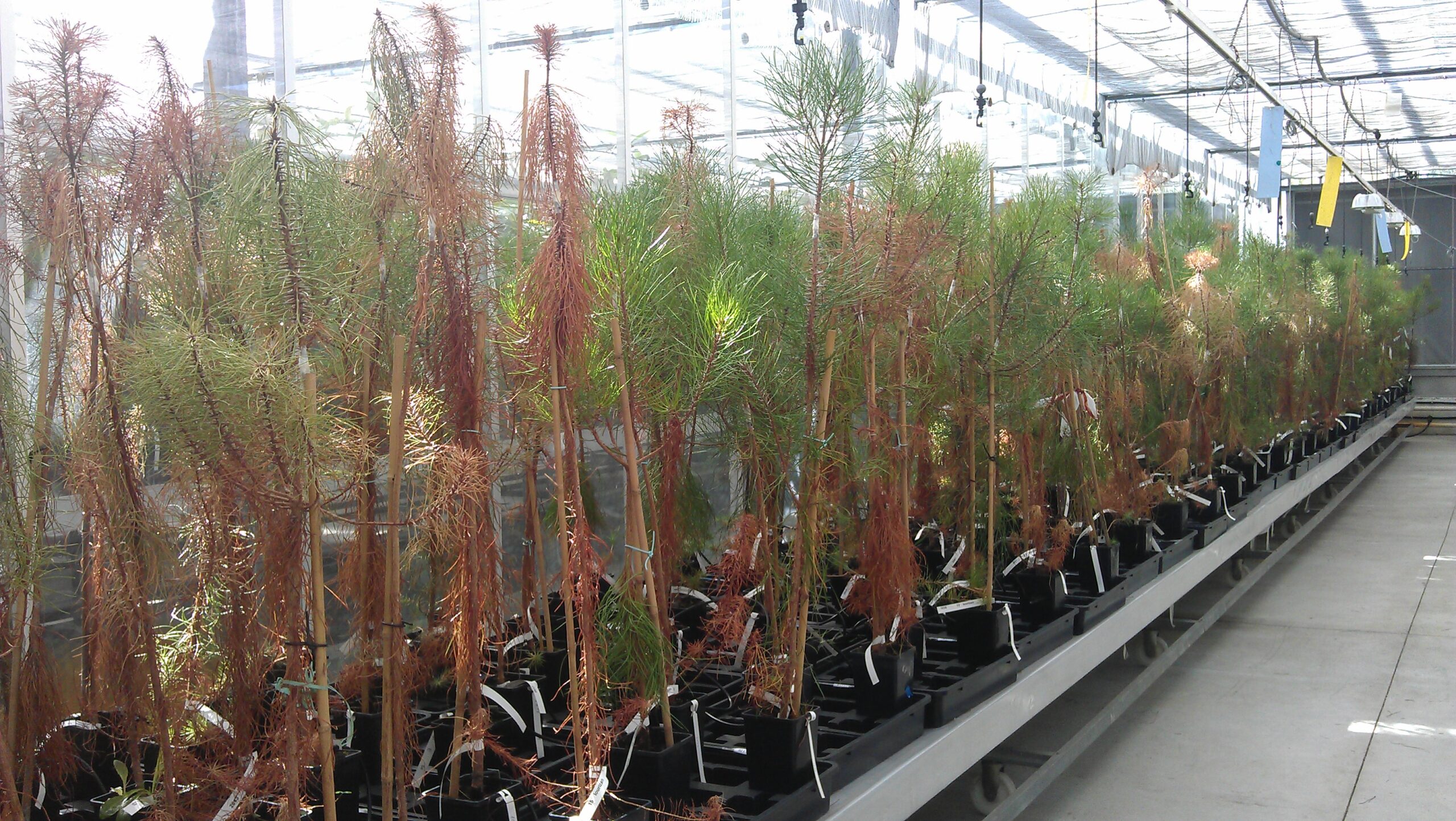

Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (pinewood nematode, PWN), the nematode that causes the pine wilt disease (PWD), is considered a very important threat to the European pine forests. It is included in the A2

RESONATE: Resilient forest value chains – enhancing resilience through natural and socio-economic responses, a four year Horizon2020 project (https://resonateforest.org/), was recently completed with two synthesis reports and three policy briefs.
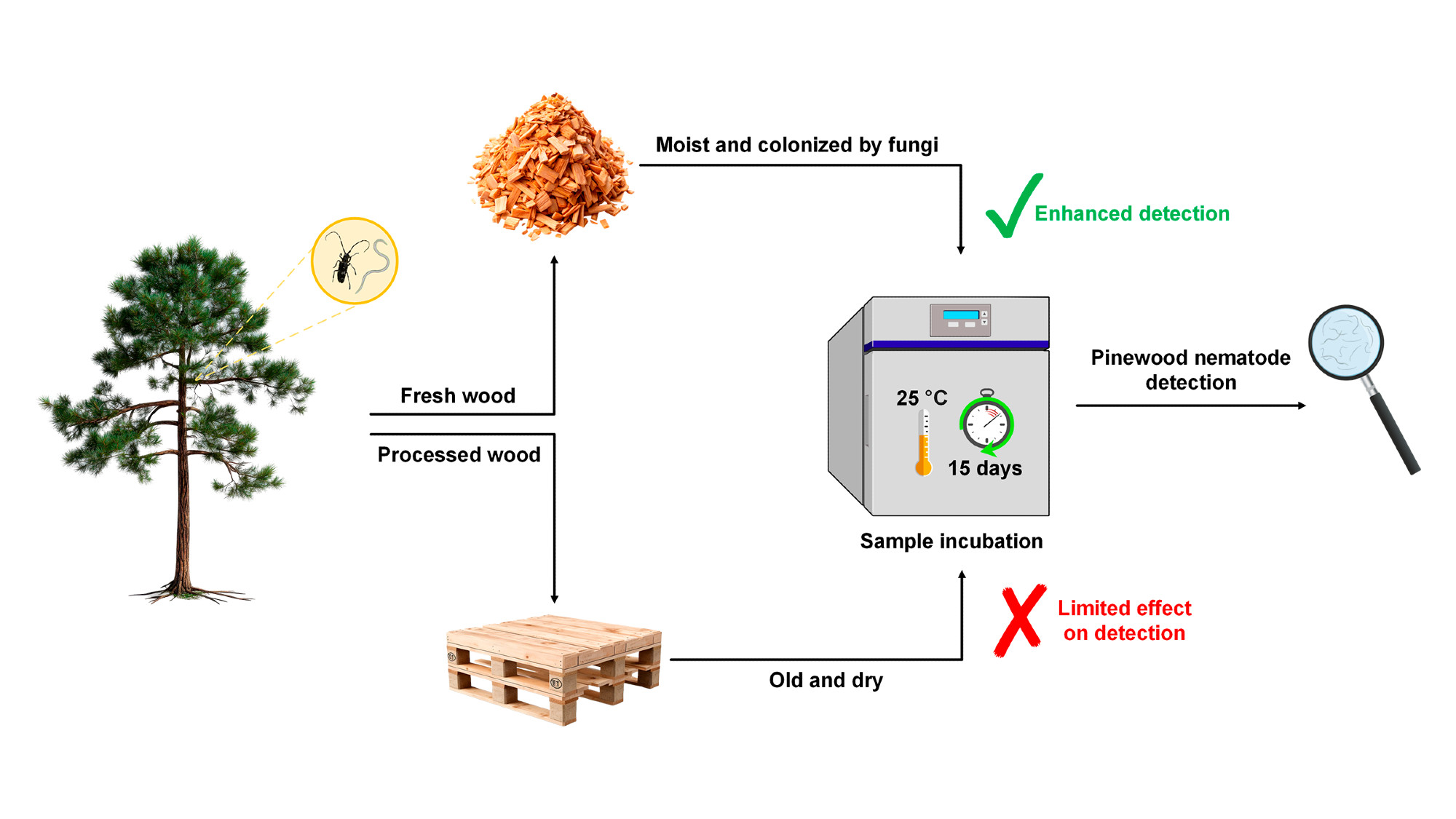
Among the most concerning threats impacting global forest ecosystems is the pinewood nematode (PWN, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner and Buhrer) Nickle), the causal agent of pine wilt disease. In Europe, effective management of

We are glad to announce the first webinar of IEFC and the new task force on Stand Complexity in Planted Forests together with the IUFRO Research Unit – 1.03.00 –

Question 1 : In your opinion, what are the main benefits of planted forests in addressing current environmental challenges, such as climate change and biodiversity loss ? We are facing

IEFC wishes you a prosperous 2025 Last November ranked as the world’s second-warmest November on record after November 2023. If La Niña weather pattern forms in 2025 global temperatures could
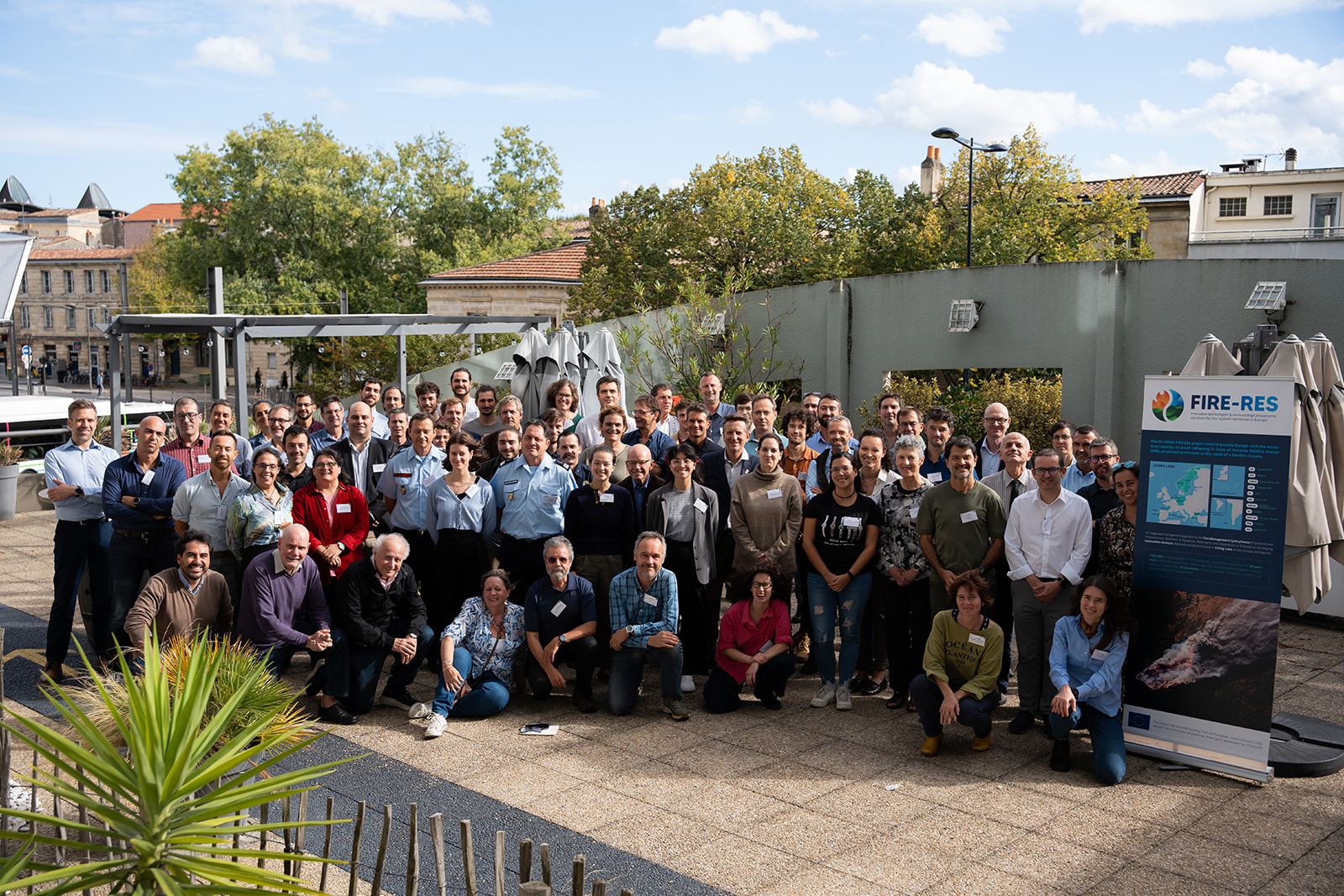

From October 8 to 10, 2024, the FIRE-RES project held its general meeting in Bordeaux and Mimizan, bringing together researchers, local stakeholders, and European partners from the 11 Living Labs.

By Faustine Zoveda, Laureana de Prado, and Thais Linhares-Juvenal, FAO The 27th Session of the International Commission on Poplars and Other Fast-Growing Trees Sustaining People and the Environment (IPC27), hosted
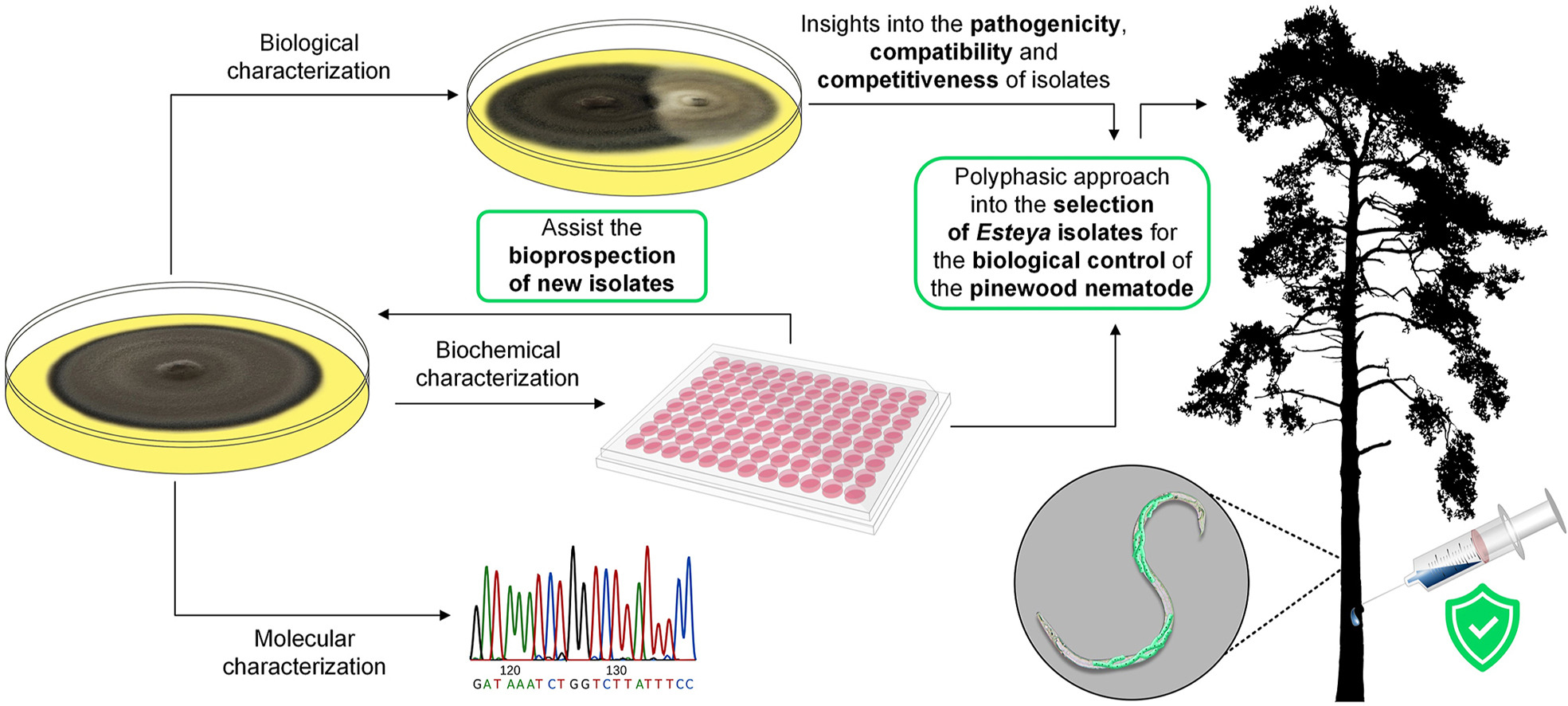
Pine wilt disease, caused by the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, is a major phytosanitary concern to pine forests worldwide. Managing pine wilt disease involves a complex logistical undertaking, with limited