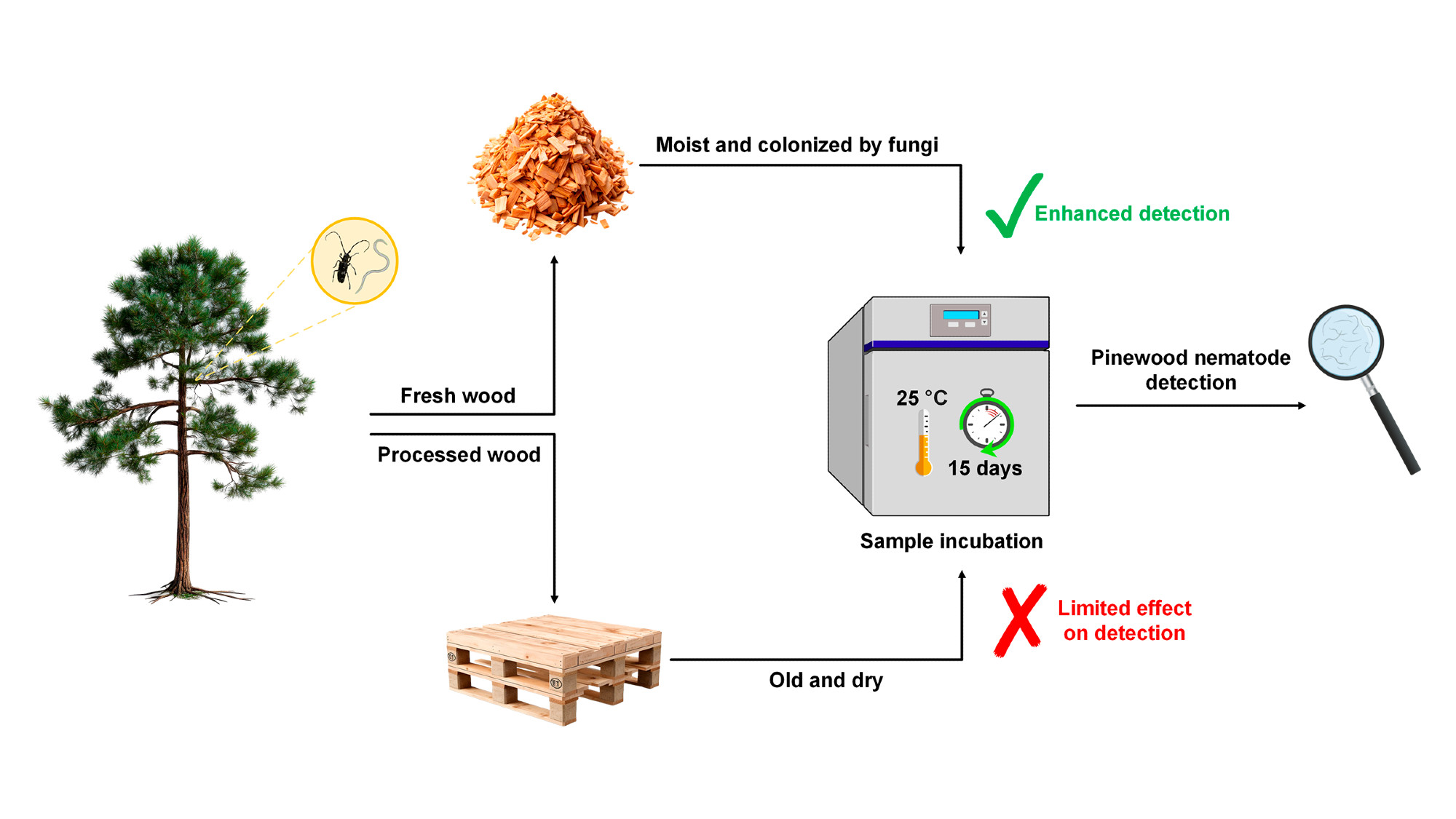
Among the most concerning threats impacting global forest ecosystems is the pinewood nematode (PWN, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner and Buhrer) Nickle), the causal agent of pine wilt disease. In Europe, effective management of this pest requires comprehensive regulatory and monitoring strategies, including the annual collection of thousands of wood samples from symptomatic trees and their surroundings, inspection of wood packaging materials like pallets, and the trapping of the insect vector, Monochamus spp., through national networks. Insects and wood samples are sent to official laboratories, where the latter are sometimes incubated at 25 °C for 15 days, aiming to maximize the probability of the detection of the nematode. This study expected to elucidate the effect of the wood incubation process on the detection of B. xylophilus by analyzing wood samples from pallets and green wood obtained from pine stands, both harbouring nematodes in adult and juvenile stages. Additionally, the investigation sought to assess how the presence of fungi, which serve as a food source for the nematodes, enables B. xylophilus to persist in treated pallet wood that is colonized by these fungi. The results indicated that the incubation period is unnecessary for detecting B. xylophilus in pallets, except when the wood is heavily colonized by fungi providing suitable nutrition for the nematodes, although such occurrences are expected to be rare. Furthermore, this study found no significant differences in population growth between the two stages of the nematode’s life cycle. This suggests that second-stage juveniles present in wood samples, despite not undergoing sexual differentiation, do not hinder the reproductive capacity of B. xylophilus. The risk of a potential infestation in treated pallet wood is unlikely if the treatment has been performed correctly, and the incubation does not contribute to increasing the probability of detecting the PWN. Conversely, for samples obtained from trees, the incubation period significantly enhances nematode detection.
The link to the paper: https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020339
A graphical representation of the paper is attached below.
David Pires, PhD Candidate